FAMILY DENTISTRY
Family Dentistry
 |
Call [450] 979-7626 Schedule your first appointment in minutes |
Dental Exam
 The oral exam includes the exam of the teeth, soft tissues (e.g., gum, tongue, cheeks), and hard tissues (e.g., bone surrounding teeth, jaw bone, palate).
The oral exam includes the exam of the teeth, soft tissues (e.g., gum, tongue, cheeks), and hard tissues (e.g., bone surrounding teeth, jaw bone, palate).
The oral exam is recommended twice a year in general.
During the exam, and as per every person’s needs, intra-oral photos as well as dental and panoramic x-rays are taken with state of the art technology. After the exam, different treatment options are presented and discussed. A treatment plan is then chosen, a plan which is adapted to your needs and suits your budget.
Please note that we offer different financial plans to help you receive the best treatments, and finally have the smile of your dreams.
Periodontics (Gums)
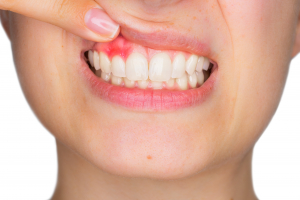
Periodontics or gum disease treatment:
- Non-surgical curettage or deep scaling to treat moderate gum disease
- Surgical curettage or deep surgical scaling to treat advanced gum disease
- Gum grafting to treat (cover) and prevent non-aesthetic receding gums
- Gum grafting to treat receding gums on sensitive teeth
- Autogenous or AlloDerm grafting
- Gum remodeling for a more beautiful smile by elongating short teeth
- Tooth exposition to treat it better
- Bone grafting preparing it for an implant
Crown
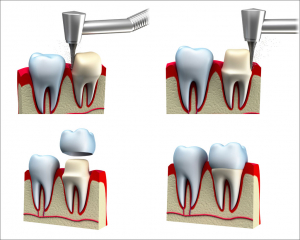 A crown is a structure made out of porcelain or composite. The crown could be partial or complete, replacing a part or the whole tooth. It protects the natural tooth, restores its function, and gives it an aesthetical look.
A crown is a structure made out of porcelain or composite. The crown could be partial or complete, replacing a part or the whole tooth. It protects the natural tooth, restores its function, and gives it an aesthetical look.
Indications for a crown:
- A tooth severely damaged by a big cavity, a filling, a trauma or a dental anomaly
- An important enamel wear
- A tooth weakened by a root canal treatment
- Crown over an implant
Endodontics (Root Canal)
An endodontic treatment is commonly called a root canal. During the root canal, the interior of the tooth is cleaned of nerves, blood vessels, and all contaminated substances. It is then prepared, sealed and filled to prevent an infection.
Indications for a root canal:
- Nerve exposure caused by a deep cavity or trauma
- Intense or chronic pain
- Tooth Infection (abscess) with or without swelling
- In prevision for some crowns
Dental Cleaning
Dental cleaning treats and prevents gingivitis. Gingivitis is the gum disease where the part that surrounds the tooth is inflamed. The signs of gingivitis are redness, bleeding, swelling, bad taste, bad breath, and pain.
During the dental cleaning, a scaling is done (tartar removal). The scaling is the part of the cleaning where the factors (plaque and tartar) causing periodontal disease are eliminated. Periodontal disease is when the gums and the bone surrounding the tooth are inflamed or infected. Signs of periodontal disease are redness, bleeding, swelling, bad taste, bad breath, cavities, teeth sensitivity, mobility or migration, and pain.
After removing the tartar, the teeth polishing is performed: this is where stains are removed to give the teeth their shine.
For children, fluoride is applied to the teeth after the dental cleaning to make the enamel more resistant to dental decay.
Dental cleaning is usually recommended twice a year. In some cases where tartar is formed more quickly, dental cleaning may be recommended more often.
Restoration (Fillings)
 A dental restoration is commonly called a filling. A dental filling replaces the damaged part of the tooth and restores its function. It is made of composite (white filling) or amalgam (silver filling). The composite dental filling gives an aesthetic look to the tooth, giving you the confidence to talk, smile and laugh freely.
A dental restoration is commonly called a filling. A dental filling replaces the damaged part of the tooth and restores its function. It is made of composite (white filling) or amalgam (silver filling). The composite dental filling gives an aesthetic look to the tooth, giving you the confidence to talk, smile and laugh freely.
Indications for a dental filling:
- A small or moderate cavity
- A broken or damaged filling
- A chipped, cracked or broken tooth
- Enamel wear
Bridge
A bridge is the traditional way to replace one or more missing teeth. The bridge improves the function and appearance of the mouth, and prevents migration of the teeth, caused by the absence of one or more teeth, as well as gum and jaw problems. A permanent bridge uses existing teeth for support (pillar), which eventually damages those teeth (see implants section for a better and more modern solution to replace one or more missing teeth). There are three types of permanent bridges: the conventional bridge, the butterfly bridge, and the implant bridge.
Indications for the bridge:
- One or more missing teeth
Surgery
- IMPLANT: (SEE IMPLANT)
- GUMS: (SEE PERIODONTICS)
- WISDOM TEETH: extraction of wisdom teeth only when it is absolutely necessary to remove them
- DAMAGED TOOTH: extraction of a damaged tooth that can no longer be saved by periodontal or dental treatment such as a filling, a root canal or a crown
- RESIDUAL ROOT: extraction of a residual root in the gum or in the bone
- REMODELING of the gum or bone in preparation for a partial or complete prosthesis
- APECTOMY or root surgery in order to save a tooth after a failed root canal treatment
Our Services